Have you been thinking of collecting 1984 quarters? Do you want to learn more about these coins before you commit? If so, this post will help you.
Table of Contents
In it, we’re going to talk about the 1984 quarter value, errors, varieties, history, and key features.
1984 Quarter Details
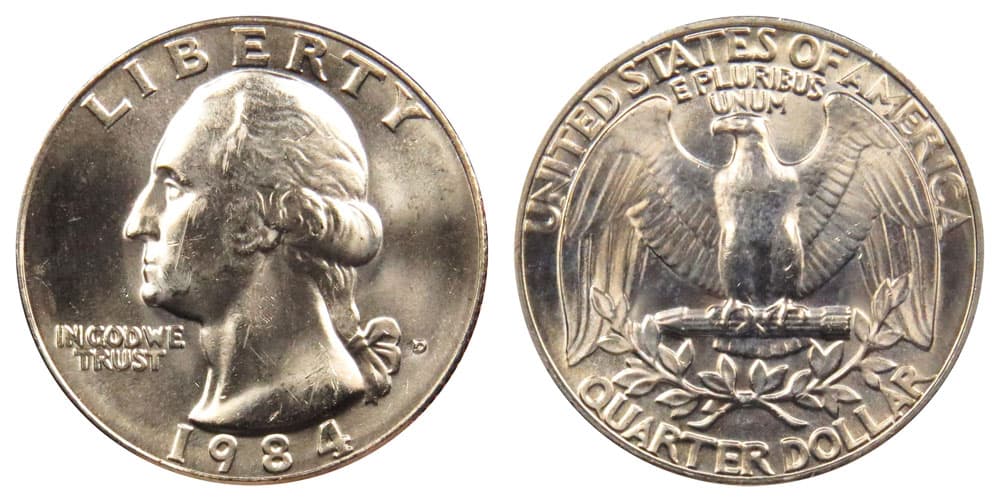

- Type: Washington Quarters
- Quantity produced: 1,226,093,170
- Minting place: Philadelphia, Denver, San Francisco
- Engraver/Designer: John Flanagan
- Mass: 5.67 g
- Composition: 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper
- Diameter: 24.3 mm
- Edge: Reeded
- Face value: 25 cents ($0.25)
The 1984 Quarter’s Obverse
One image dominates the 1984 quarter’s obverse; George Washington’s left-facing profile. It has an “IN GOD WE TRUST ” engraving under his chin and a mint mark behind his neck.
The design also features two legends along its rim. There’s “LIBERTY” along the top rim and “1984” along the bottom one. The top legend starts in front of Washington’s forehead and ends at the back of his head.
On the other hand, the bottom legend is right below where his neck cuts off.
The 1984 Quarter’s Reverse
The dominant feature of the 1984 quarter’s reverse side is an eagle. This bird is facing left, has outstretched wings, and stands on a bundle of arrows. This bundle lies on top of a wreath made of olive branches.
Also, the motto “E PLURIBUS UNUM” is written above the eagle’s head. This inscription lies below a legend along the top rim saying “UNITED STATES OF AMERICA”. Another legend appears along the coin’s bottom rim, saying “QUARTER DOLLAR”.
A sculptor called John Flanagan designed and sculpted both sides of the 1984 quarter.
The 1984 Quarter’s Other Features
1984 quarters are round coins with a 24.3 mm diameter and a reeded edge. It has a mass of 5.67 grams and a composition of 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper.
To achieve this composition, the mint coated a pure copper core with a layer of 25% nickel and 75% copper.
Also Read: Top 16 Most Valuable Modern Quarters Worth Money
Value Chart
| 1984 Quarter Value Chart | |||
| Grade | 1984 “P” Quarter | 1984 “D” Quarter | 1984 “S” Quarter |
| XF45 | $0.25 | $0.25 | N/A |
| MS60 | $1 | $1 | N/A |
| MS65 | $14 | $28 | N/A |
| MS67 | $550 | $900 | N/A |
| PR67 | N/A | N/A | $6 |
| PR70 | N/A | N/A | $40 |
1984 Value and Varieties Guide
1984 “P” Quarter Value

- Series: Washington Quarters
- Year: 1984
- Mintage: 676,545,000
- Mint Mark: P
- Minting place: Philadelphia
- Edge: Reeded
- Mass: 5.67 g
- Diameter: 24.3 mm
- Composition: 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper
- Designer: John Flanagan
- Face value: 25 cents ($0.25)
- Current value: $0.25 to $1,150
The Philadelphia facility minted 676,545,000 1984 quarters. All of these were regular-strike coins and had a mint mark. Because of their high mintage, these coins are readily available.
As such, a low-grade 1984 quarter will usually cost a few cents. Even an MS60 will only cost $1 per piece while an MS65 will go for $14. Ultimately, only coins with a grade of MS66 and above can sell for hundreds of dollars.
1984 “D” Quarter Value
- Series: Washington Quarters
- Year: 1984
- Mintage: 546,483,064
- Mint Mark: D
- Minting place: Denver
- Edge: Reeded
- Mass: 5.67 g
- Diameter: 24.3 mm
- Composition: 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper
- Designer: John Flanagan
- Face value: 25 cents ($0.25)
- Current value: $0.25 to $1,350
The Denver facility minted 546,483,064 1984 quarters. These were all regular-strike coins and had a mint mark. Since their mintage is lower than that of the Philadelphia coins, they can be more expensive than them, especially in mint state.
However, they are still affordable and even cheap in low grades. For instance, an XF45 or AU50 can just cost a few cents. On the other hand, an MS65 can sell for around $28. Usually, only grades above MS66 can sell for over $100.
1984 “S” Quarter Value
- Series: Washington Quarters
- Year: 1984
- Mintage: 3,065,110
- Mint Mark: S
- Minting place: San Francisco
- Edge: Reeded
- Mass: 5.67 g
- Diameter: 24.3 mm
- Composition: 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper
- Designer: John Flanagan
- Face value: 25 cents ($0.25)
- Current value: $4 to $55
The San Francisco facility minted 3,065,110 1984 quarters. All of these were proof coins and had a mint mark. As such, each of them had a shiny polished surface. And since they were properly stored, they are still in good condition to date.
As such, several of them are graded ultra cameo or deep cameo; this is the highest grade a proof can get. But even though their mintage is lower than that of the quarters produced in Denver and Philadelphia that year, it’s still high for proof coins.
As such, they are not as expensive as you expect proofs to be. A deep cameo PR65 can sell for only $5. Even a deep cameo PR70 can sell for only $55. Currently, the most expensive PCGS deep cameo to be auctioned is a PR70 sample that sold for $380 in 2003.
Also Read: Top 15 Most Valuable Quarters In Circulation
1984 Quarter History
1984 quarters are part of the Washington quarter series. This was launched in 1932 and it’s still minted to date. As its name suggests, all the coins in it have an image of George Washington on their obverse side.
George Washington was an American founding father and the first president of the United States. He was born on 22nd February 1732 and died on 14th December 1799. Because of how important he was to the American people, his birthday was made a holiday.
This began in 1885 when Congress decided to make the 22nd of February a holiday for federal workers. This was the first holiday ever designated to commemorate someone’s birthday.
In 1971 another law was put in place to make the third Monday of every February President’s Day. This is a holiday celebrating both Washington’s and Lincoln’s birthdays; it’s celebrated to date.
So it was not surprising that Congress wanted to honor Washington’s birthday by placing him on a coin in 1932. After all, Lincoln had already been placed on the penny; he was the first real person to appear on a coin.
However, the choice to have a coin with Washington’s image was ironic; he had always been against it and considered it colonial. Either way, the committee responsible for this decision quickly decided to put his face on the half dollar.
The committee had even started talking to Laura Fraser about commissioning her to do the coin’s designs. They had chosen her because of her previous work.
However, things quickly changed when Congress decided to put Washington on the quarter instead. And soon enough, a new designer was chosen; John Flanagan. His obverse and reverse designs remained on the quarter until 1998.
However, these designs have changed severally since 1999. The first change featured around 50 reverse designs that had images depicting different states. The coins with these designs were called the 50 states quarters.
In 2010, the mint started to produce quarters featuring elements of the United States national parks and sites. These were called America the Beautiful quarters.
More recently, the mint has started featuring the images of prolific American women in its quarters. These current coins are called American Women quarters. They have a composition of 8.33% nickel and 91.67% copper.
This composition has been used since 1965. Before that, Washington quarters were made of 90% silver and 10% copper. As of now, only special proof sets for collectors are made of silver. This has been happening since 1976.
1984 Quarter Grading
Accurately grading 1984 quarters requires contacting an expert. For best results, send your coin to a widely-known grading agency like NGC or PCGS. Try to figure out if you have a special coin beforehand though. And ensure you only send coins that look new-ish.
Otherwise, you will waste your money paying grading fees only to end up selling the coin for a few cents. And remember, you don’t have to grade a coin before selling it.
Also Read: 10+ Rarest State Quarter Errors Lists (Worth Much Money!!!)
List of 1984 Quarter Errors
1. 1984 Quarter Broad Struck

A broad strike error is a result of striking a coin out of the collar. This creates a coin that spreads out too much and can even have a strange shape. This can make a coin more valuable.
For instance, an MS64 1984 P quarter with this error can end up selling for a little over $15.
On the other hand, an MS67 1984 D quarter with the same error can sell for over $760.
Keep in mind that a similar coin that’s just a grade lower (MS66) can end up selling for around $65.
2. 1984 Quarter Struck Off-center
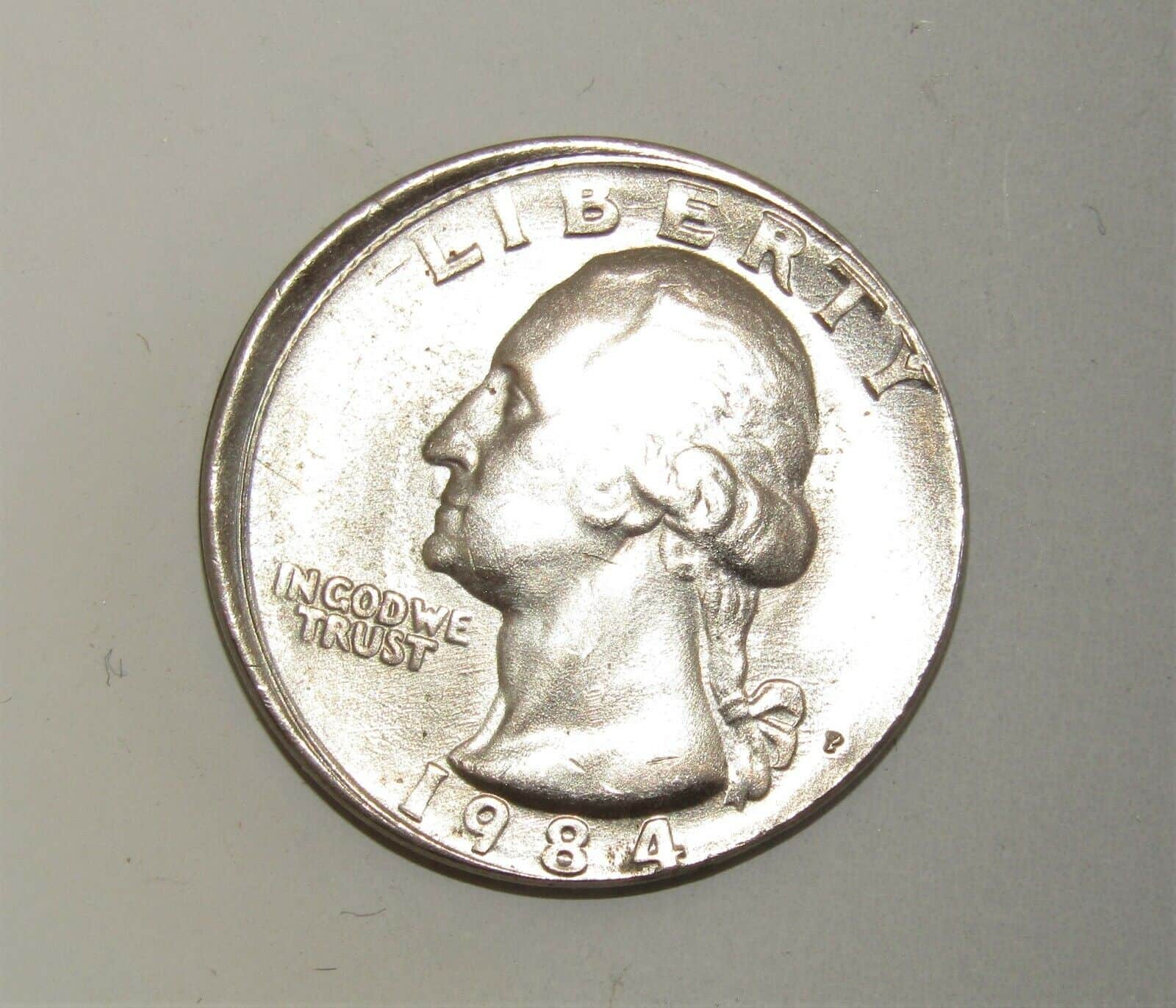

When a coin’s design isn’t struck on it in a centered fashion, it ends up with an off-center strike error. The severity of this error is usually measured by the percentage by which the strike is off-center.
After all, the bigger this percentage, the more noticeable the error and the more valuable the coin. An NGC MS63 1984 P quarter that’s been struck 15% off-center can sell for a little over $40.
But a similar coin with a higher off-center percentage can sell for a little over $60. On the other hand, a version with a higher grade (MS66) and a 10% off-center strike can sell for over $80.
3. 1984 Quarter Double Struck with Second Strike Off-center

As its name suggests, a double strike error is the result of a blank being struck twice. This usually happens when something prevents the coin from leaving the striking chamber fast enough after the first strike.
When the second strike isn’t on-center, it creates a more noticeable and valuable coin. An NGC MS64 1984 P quarter that has been double-struck with an off-center second strike can sell for over $160.
1984 Quarter FAQ
Is a 1984 quarter rare?
No, the 1984 quarter isn’t rare. It is still readily available because of its high mintage. Also, it was only minted a few decades ago so there are still many of these coins in mint state.
To make matters worse, 1984 quarters aren’t prone to remarkable errors that make them super valuable. That’s why professionally grading these quarters is risky; you can simply end up wasting money you won’t get back.
How can I tell if my coin is worth money?
You can tell whether a coin is worth a good amount of money by finding out its grade, mintage, type (proof/regular strike), and errors.
Once you have this information, you can find out how much money similar coins have sold for and price your coin accordingly.
Are coins easy to sell?
Yes, selling your coins is easy; there are several ways to do it. For one, you can take your coin to a local coin dealer/shop. Alternatively, you can sell your coin on an online store like eBay or Etsy. You can even sell it at a big auction house if it’s a valuable find.
At what age do coins gain value?
For the most part, age doesn’t affect the value of a coin.
Does a 1984 quarter have silver?
No, these quarters don’t have silver. The mint stopped using silver in its quarters in 1964. This was because of the rising silver prices at the time. All the quarters that came after had 91.67% copper and 8.33% nickel.
What year is the rarest Washington quarter?
The rarest Washington quarter year is 1932. This is because it had the lowest Washington quarter mintage and was also the year that this quarter series launched. The rarest variety of the 1932 Washington quarter is the San Francisco (S) type.
There were less than ½ million of these quarters minted. The Denver quarters were a little more than these. On the other hand, the Philadelphia quarters were a little over 5 million.



